Benchmark Results¶
The benchmark will produce results like in the sample below.
For more details on the steps required to produce these results, please refer to Executing the LUBM Extended Version.
Loading Data¶
Import data provided in the following combinations of file format and data compression.
For LUBM 1000, the data is provided in one single file. However, tests can be also done for data split across smaller files.
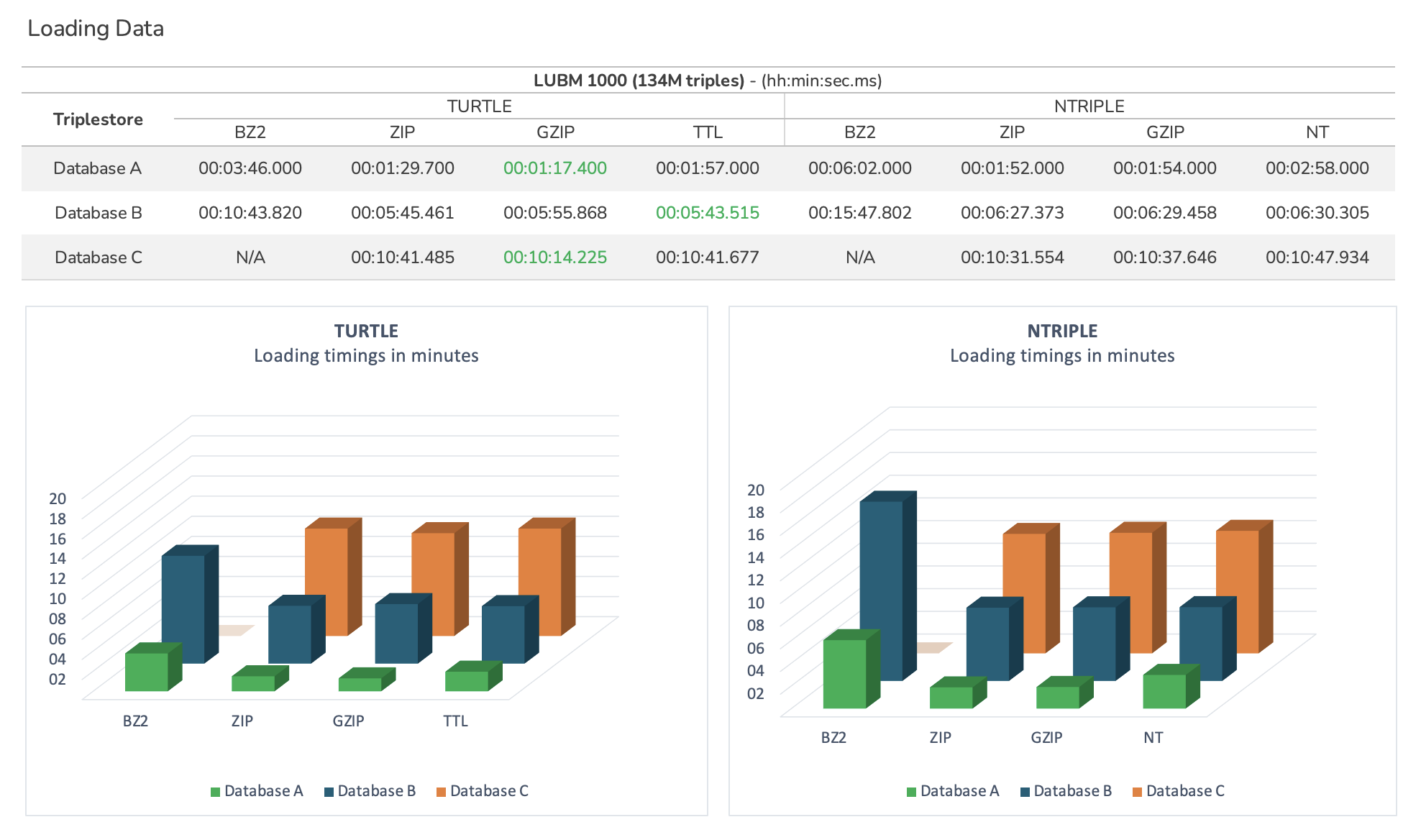
Note: Statistics update is disabled during the data load.
Materialising and Optimising¶
The materialisation of inferred facts happens when importing the ontology and rules 2 and 9 and only applies to materialisation-based triplestores.
Optimisation refers mainly to statistics update, which is required for optimum query performance after the data import is complete.
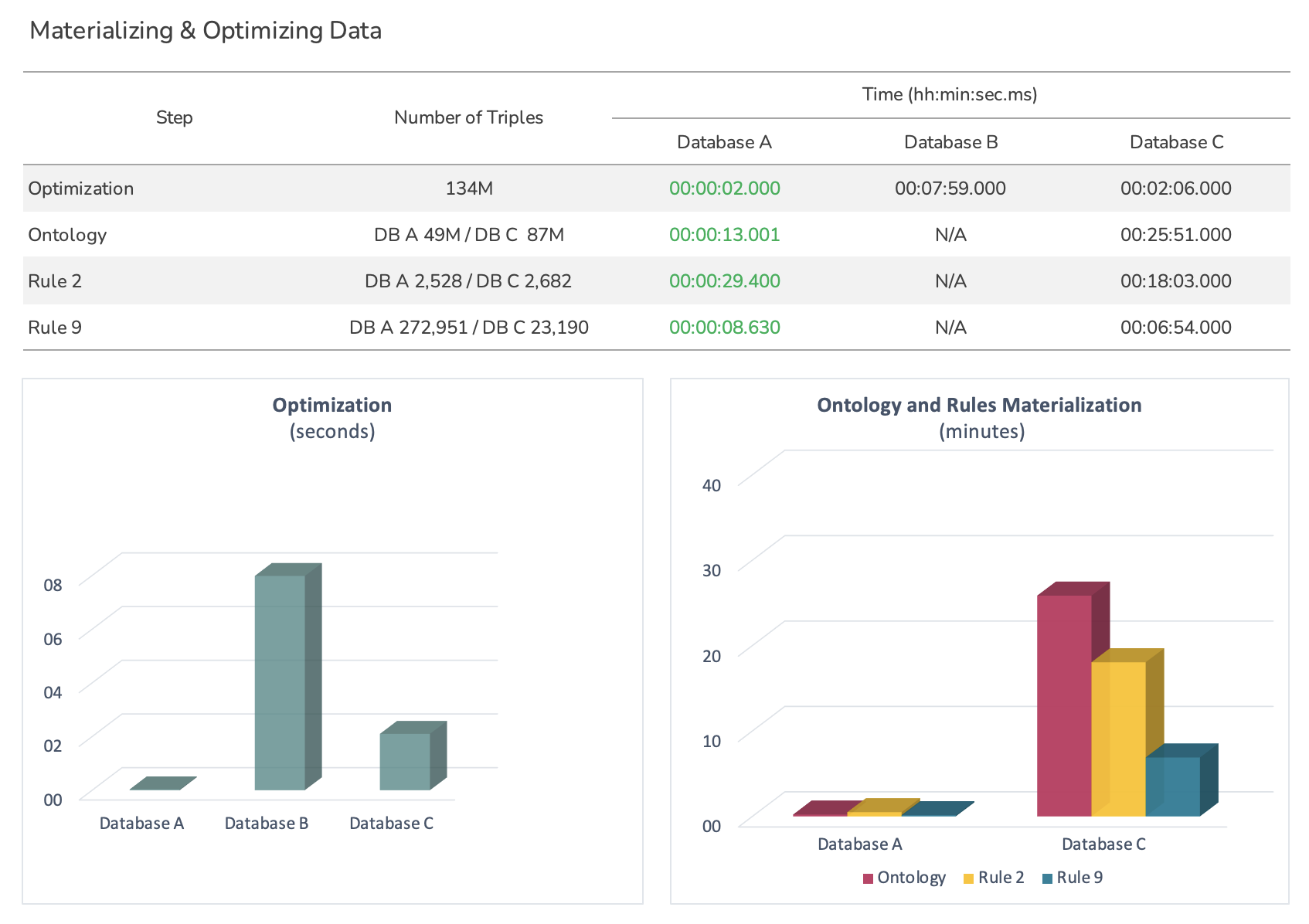
Note: The Optimisation step may represent different things in each triplestore, however we always make sure that the statistics update is included. Most efficient OWL 2 profile is attempted for efficiency of reasoning if they produce the expected query results.
Original Queries¶
Execute the original queries provided with the LUBM benchmark.
The results are calculated as the average of multiple executions after a few warmup runs.
The following illustration shows that the original queries provided by the LUBM benchmark were too simple and therefore not good enough to challenge any of the triplestores tested. From the original LUBM perspective, any triplestore would most likely produce successfull results, regardless of the test dataset size.
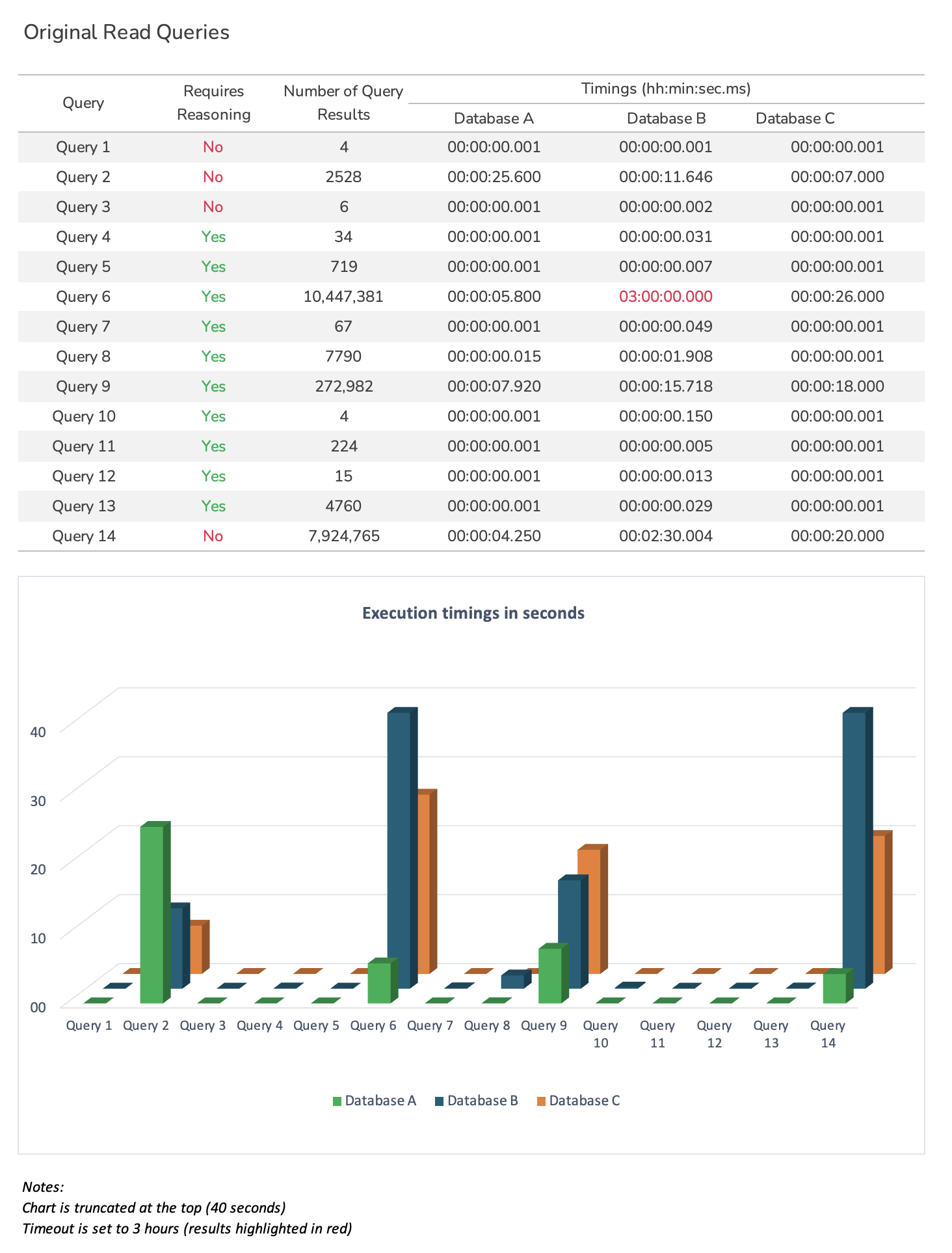
Note: Queries are executed through the triplestore CLI and REST API when available. We expect backward-chaining triplestores to respond a bit slower as they calculate reasoning at query time.
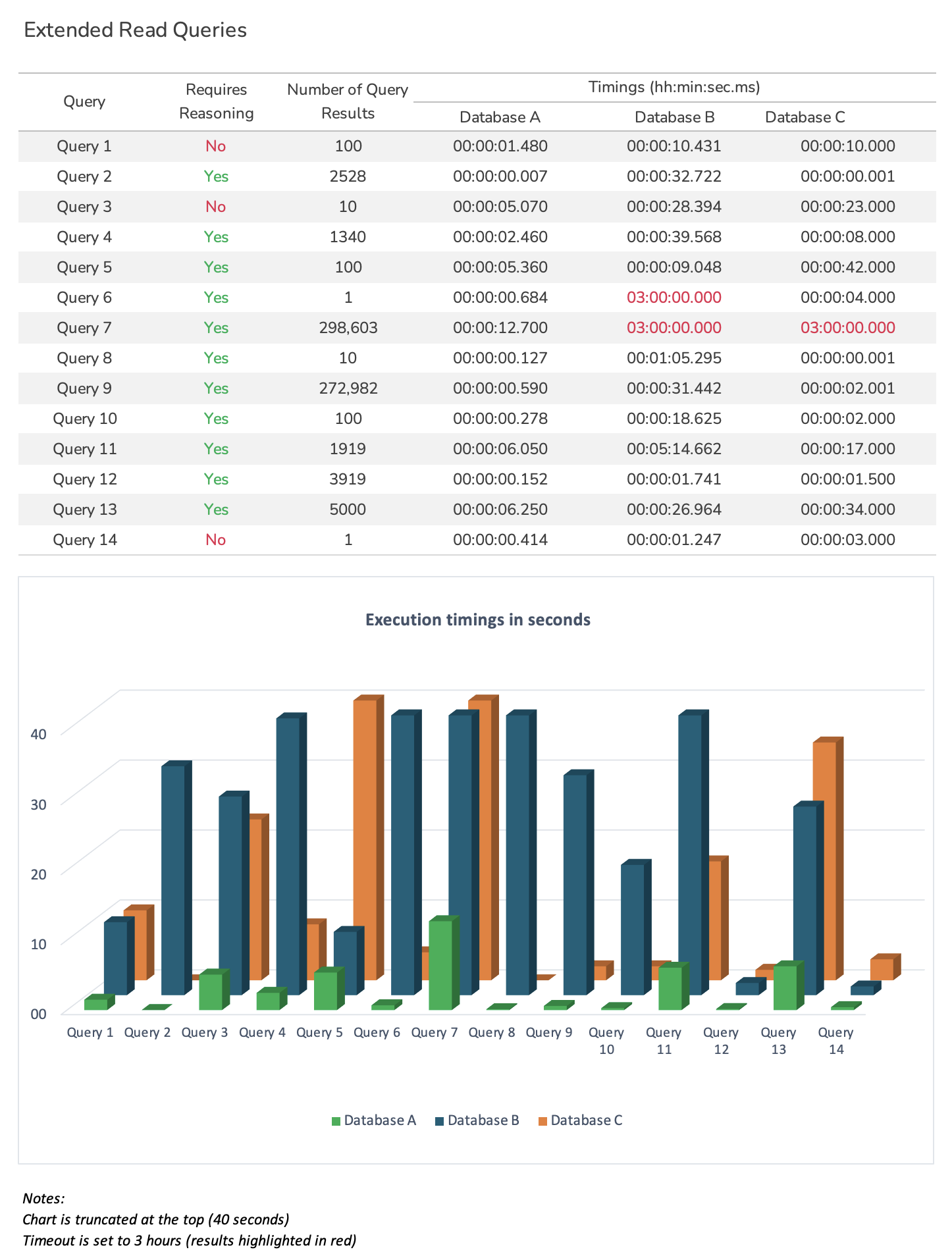
Extended Queries¶
These queries include more realistic business-like use case scenarios. For more details on the SPARQL changes done by agnos.ai, please refer to the "Extended" tab in each query on the LUBM SPARQL Statements page.
The following results illustrates well the performance impact of the more complex queries on each triplestore in relation to the results seen in the previous chart.
Update Queries¶
This test contains updates and selects which are executed in pairs. The select query is designed to read the triples affected by the update and it is executed immediately after the update transaction is committed. No warmup runs are executed for this test. Update queries include deletes and inserts to different named graphs.
At this stage "auto update statistics" is turned on in order to assess its impact on updates and subsequent reads.
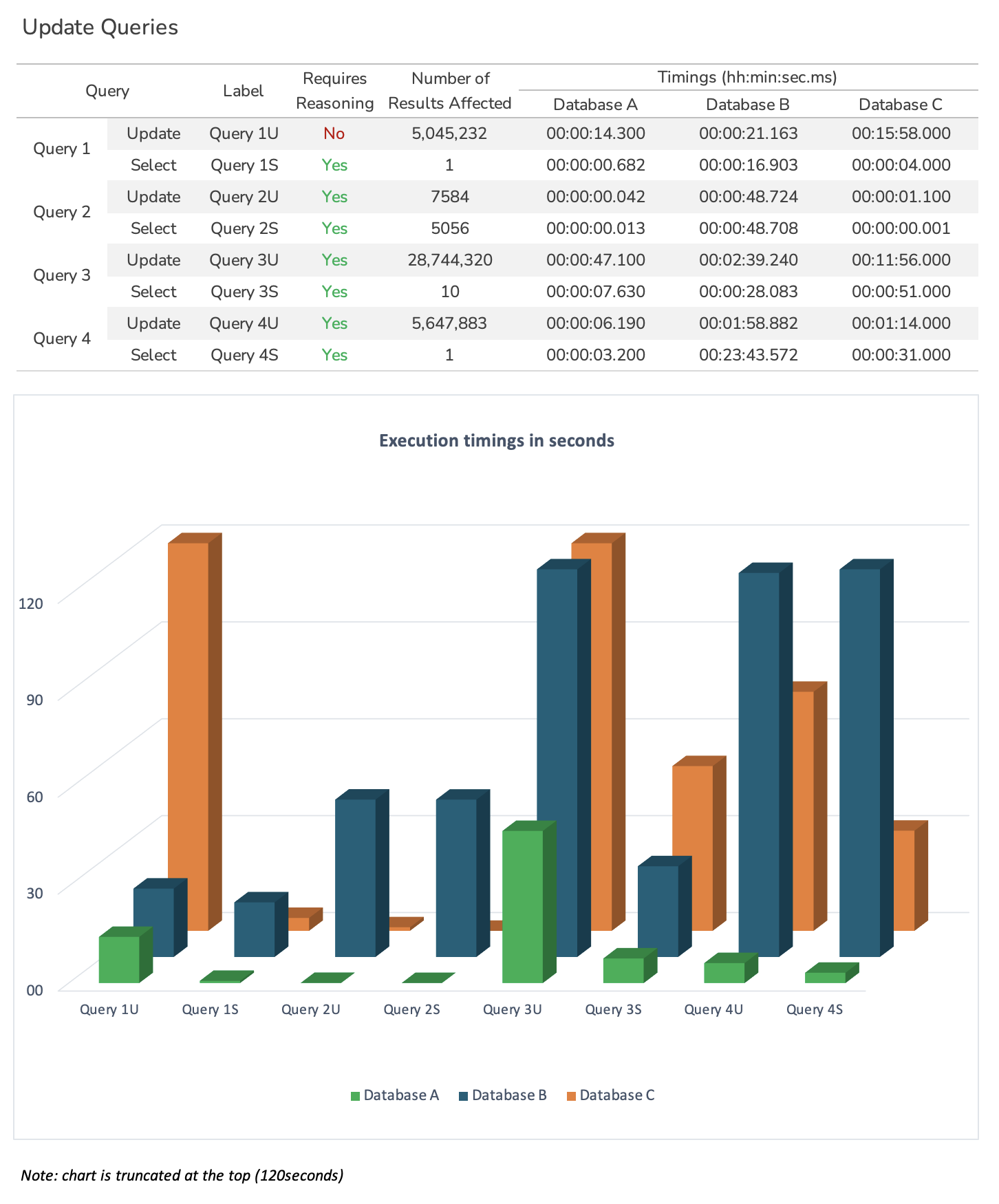
Note: A performance impact is expected on forward-chaining materialisation-based triplestores, however, such an impact may also happen on backward-chaining non-materialised triplestores, due to the required amount of data that needs to be read in preparation for the update operation.